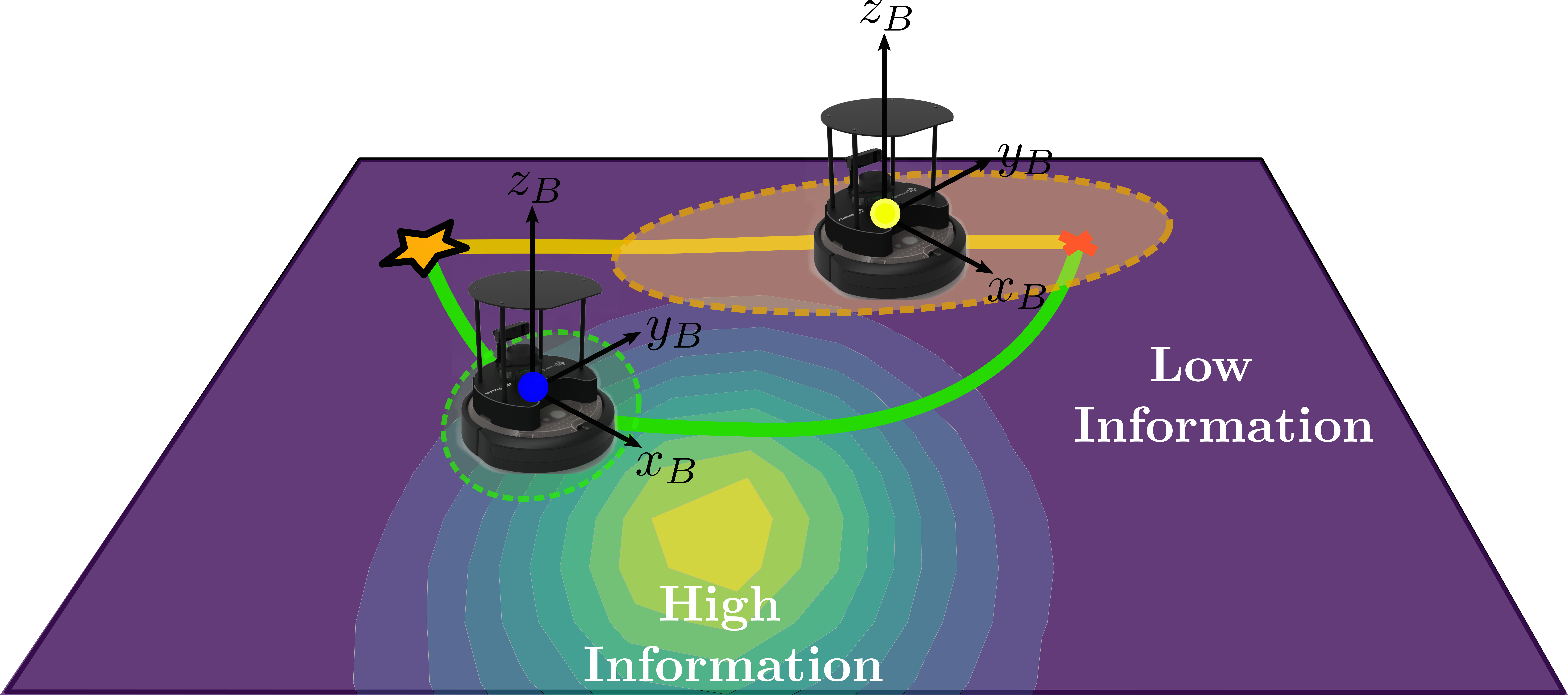
Overview
Although many outdoor autonomous robotics systems rely on GPS, there are some situations or applications where GPS signal is unavailable, e.g., navigation in an underwater environment, receiving a degraded or jammed GPS signal. One solution to this GPS-denied navigation is magnetic anomaly-based navigation, which allows robots to localize based on a series of magnetometer readings and a pre-known magnetic field map. In this project, we focus on developing information-driven active localization methods that plan a path for reducing localization uncertainty.
Research Goals
- Passively sensed navigation on ground robots that leverage maximum information available in a priori maps
- Wholistic approach for mapping and localization in magnetic scalar field maps
- Object and agent detection for passive sensing
Related Publications
- J. H. Ramos, J. Shin, K. Volle, P. Buzaud, K. Brink and P. Ganesh, “Information-Aware Guidance for Magnetic Anomaly based Navigation,” 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 2022, pp. 6347-6354, doi: 10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981709.
- Penumarti, A., Iyer, N., Park, L., Waters, K., Ramos, J., & Shin, J. (2025). Neural Network-Based Magnetometer Sensor Model for Virtual Magnetic-Based Navigation Testbed. In AIAA SCITECH 2025 Forum (pp. 0562).
Research Team
UF Team: Aditya Penumarti, Nikhil Iyer Jane Shin, Humberto Ramos (UF REEF), External Collaborators: Kristy Waters (Previously UF REEF, Now AFRL Eglin), Kevin Brink
Acknowledgement
This work is partially supported by Air Force Research Lab through FA8651-22-F-1052.